JASRACの分配の仕組み
音楽をご利用になる皆さまから
お支払いいただいた使用料は
権利者の皆さまへ適正に分配されます。
このページではJASRACの分配の仕組みを
詳細に説明します。
- TOP
- JASRACについて
- JASRACの分配の仕組み
分配ルールの基本
使用料の分配は、「著作物使用料分配規程」(分配規程)に基づき、毎年度6月、9月、12月、3月の4回の分配期に分けて行われます。分配規程では、利用のされかた(利用形態)ごとに分配期・分配対象使用料・分配対象著作物などを定めています。
使用料が作詞者、作曲者、音楽出版社に届くまで
1つの作品には、作詞者、作曲者、編曲者、訳詞者などの著作者や音楽出版社といった、さまざまな権利者が関わっています。
JASRACが国内の利用者から受け取った使用料および外国の著作権管理団体から送金された使用料が、その作品の関係権利者に届くまでを説明します。
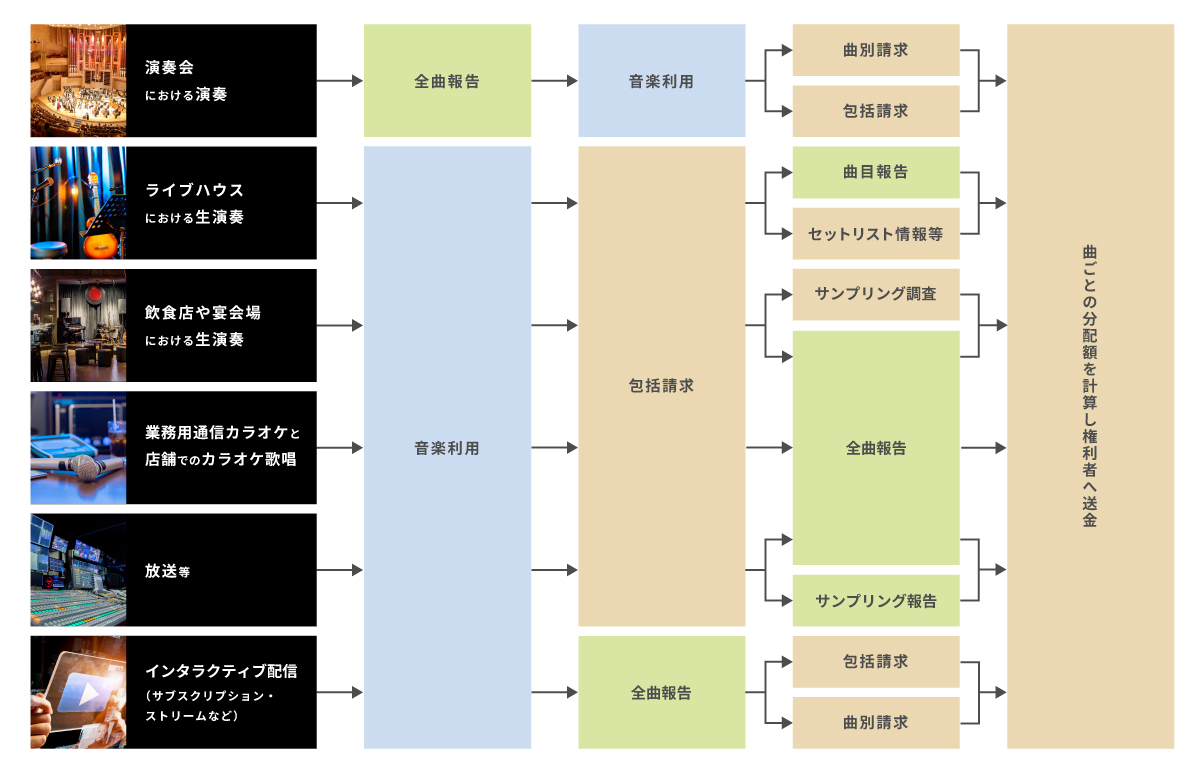
主な利用形態ごとの許諾・請求・分配の仕組み
利用者から受け取った使用料が、著作者や音楽出版社など権利者の方々に届くまでの仕組みを利用形態別に説明します。
お問い合わせフォーム
JASRACインフォメーションデスク
お問い合わせフォーム